Adjectives are an important part of English. They describe things and make our sentences more interesting. But what do we do when we want to compare things? That’s when we use comparative and superlative adjectives! In this guide, we will explain the rules, give lots of examples, and help you understand how to use these adjectives the right way.
Contents
What Are Comparative and Superlative Adjectives?
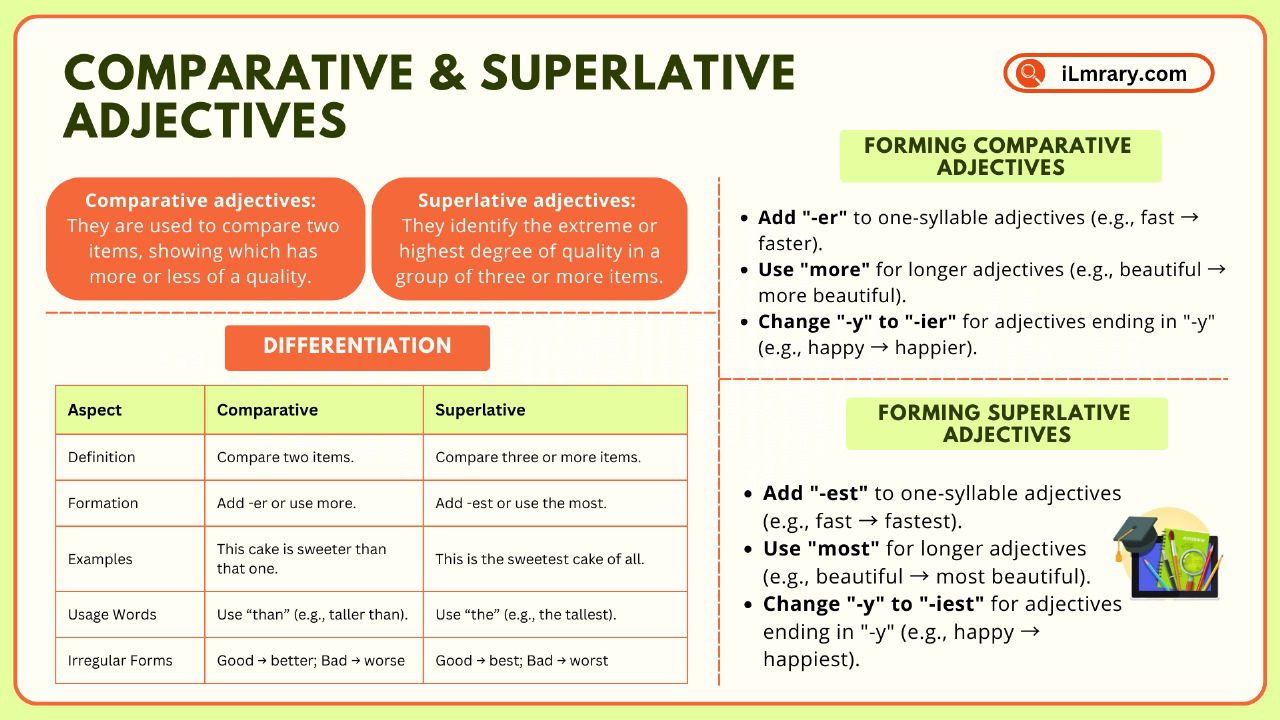
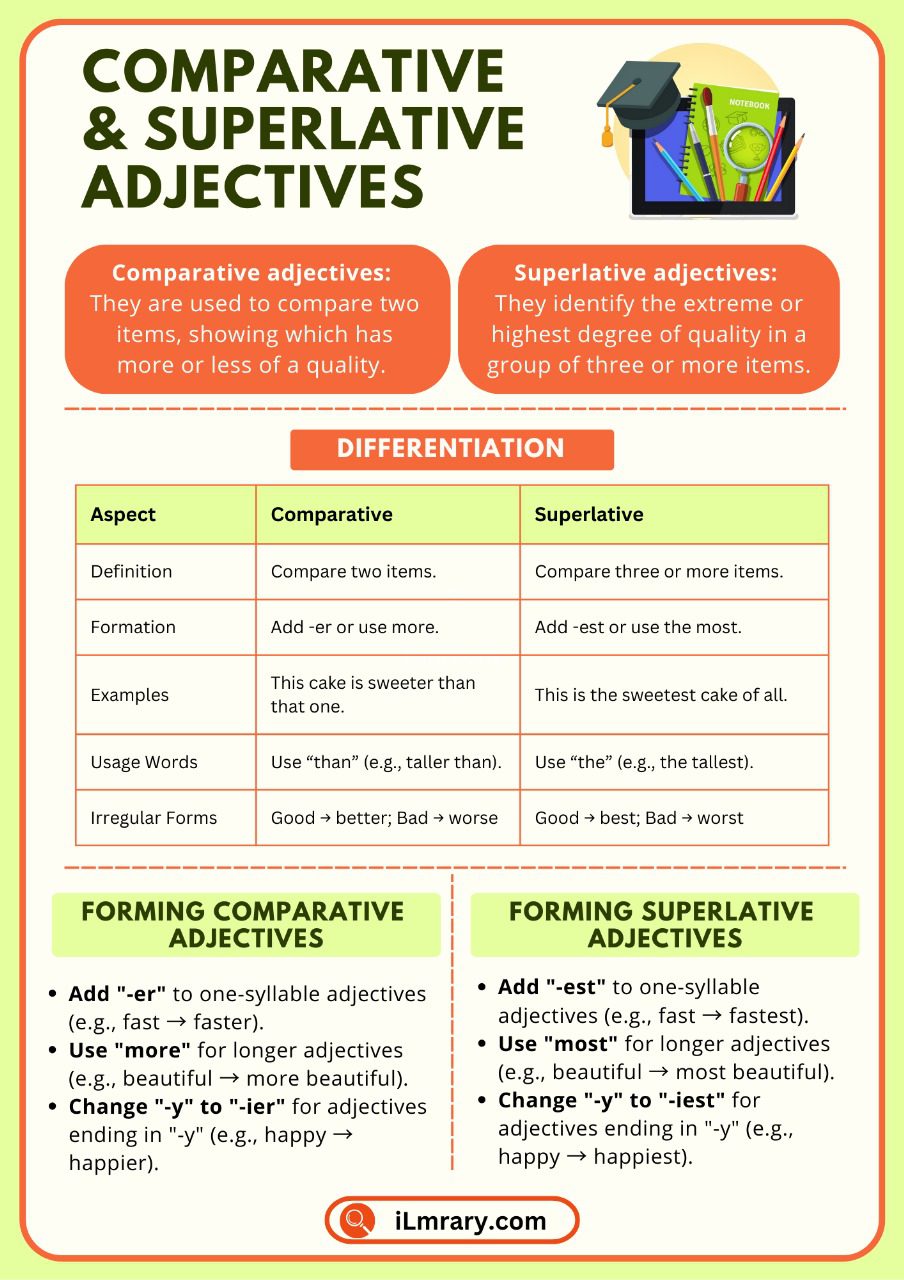
Comparative and superlative adjectives are tools that help us make comparisons. They allow us to describe how one thing is different from another or how something stands out among a group. Simply put:
Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two items, showing which has more or less of a quality.
For instance:
- This road is narrower than that one.
- My cat is quieter than yours.
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives identify the extreme or highest degree of quality in a group of three or more items.
For Example:
- She is the smartest student in the class.
- This is the coldest day of the year.
Difference Between Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
We can use a quick reference chart to summarize the differences between comparative and superlative adjectives. Moreover, this will help you identify their uses, formation rules, and examples at a glance. Understanding these distinctions will make your communication clearer and more precise.
| Aspect | Comparative | Superlative |
| Definition | Compare two items. | Compare three or more items. |
| Formation | Add -er or use more. | Add -est or use the most. |
| Examples | This cake is sweeter than that one. | This is the sweetest cake of all. |
| Usage Words | Use “than” (e.g., taller than). | Use “the” (e.g., the tallest). |
| Irregular Forms | Good → better; Bad → worse | Good → best; Bad → worst |
Irregular Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Not all adjectives follow the regular rules of adding -er, -est, or using more and the most. Some adjectives are irregular, meaning their comparative and superlative forms are completely different words.
Common Irregular Forms
| Base Form | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| Good | Better | Best |
| Bad | Worse | Worst |
| Far | Farther/Further | Farthest/Furthest |
| Little | Less | Least |
| Many/Much | More | Most |
Rules for Irregular Adjectives
1. Good → Better → Best
-Comparative:
(Better is used when comparing two things.)
- This book is better than the one I read last week.
-Superlative:
(Best is used to describe the highest quality.)
- She is the best singer in the competition.
2. Bad → Worse → Worst
-Comparative:
(Worse is used when comparing two items.)
- The weather today is worse than yesterday.
-Superlative:
(Worst indicates the lowest quality.)
- That was the worst movie I have ever seen.
3. Far → Farther/Further → Farthest/Furthest
-Comparative:
(Farther refers to physical distance.)
- This city is farther than the previous one we visited.
-Superlative:
(Both farthest and furthest can indicate the greatest distance, either literal or figurative.)
- Farthest: Of all the planets, Neptune is the farthest from the Sun in our solar system.
- Furthest: Her ideas were the furthest from what we had originally planned for the project.
4. Little → Less → Least
-Comparative:
(Little changes to less when comparing smaller amounts.)
- I have less time than you.
-Superlative:
(Least indicates the smallest amount.)
- This is the least interesting option available.
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Forming Comparative Adjectives
To form comparative adjectives, the rules depend on the length of the adjective. Here are the main guidelines:
1. One-Syllable Adjectives
Add -er to the end of the adjective.
- Tall → taller (e.g., John is taller than Mark.)
- Fast → faster (e.g., This car is faster than that one.)
2. Two-Syllable Adjectives (Ending in “-y”)
Change the “-y” to “-i” and add -er.
- Happy → happier (e.g., She looks happier today than yesterday.)
- Busy → busier (e.g., I am busier this week than last week.)
3. Adjectives with Two or More Syllables
Use “more” before the adjective instead of adding “-er.”
- Beautiful → more beautiful (e.g., This park is more beautiful than the last one.)
- Expensive → more expensive (e.g., This watch is more expensive than mine.)
Forming Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives show that something has the highest degree of quality among three or more items. Here’s how to form them:
1. One-Syllable Adjectives
Add -est to the end of the adjective.
- Tall → tallest (e.g., He is the tallest in the team.)
- Fast → fastest (e.g., This is the fastest car here.)
2. Two-Syllable Adjectives (Ending in “-y”)
Change the “-y” to “-i” and add -est.
- Happy → happiest (e.g., She is the happiest person I know.)
- Busy → busiest (e.g., This is the busiest day of the year.)
3. Adjectives with Two or More Syllables
Use “the most” before the adjective.
- Beautiful → the most beautiful (e.g., This is the most beautiful sunset I’ve ever seen.)
- Expensive → the most expensive (e.g., That is the most expensive dress in the shop.)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Learning comparative and superlative adjectives can be fun, but some common pitfalls might trip you up. Let’s take a look at how to avoid them:
1 – Using “more” and “-er” Together
- Incorrect: This is more faster than that.
- Correct: This is faster than that.
2 – Forgetting “the” with Superlatives
- Incorrect: He is tallest in the class.
- Correct: He is the tallest in the class.
3 – Overusing Superlatives
- Incorrect: This is the tallest of the two.
- Correct: This is the taller of the two.
Example Sentences
Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two things or people. Usually, they end in “-er” or use “more” before the adjective.
- My house is bigger than yours.
- She is more intelligent than her brother.
- This exam was easier than the last one.
- This book is more interesting than the other one.
- His car is faster than mine.
- I think this movie is better than the one we saw last week.
- The blue dress is prettier than the red one.
- This pizza is cheaper than that pizza.
- Her explanation was clearer than his.
- The weather today is warmer than yesterday.
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives are used to show that something is the most or least of a group. They often end in “-est” or use “most” before the adjective.
- She is the smartest student in the class.
- This is the most delicious cake I’ve ever eaten.
- He is the fastest runner in the competition.
- This is the oldest building in the city.
- That was the worst movie I’ve seen in years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Now that you have a solid understanding of comparative and superlative adjectives, it’s time to dive deeper into some of the most common questions learners have. Let’s take a closer look at some frequently asked questions.
1 – What is the difference between comparative and superlative adjectives?
Comparative adjectives compare two things, while superlative adjectives describe something that stands out as the best or worst among three or more items.
2 – How do I form comparative adjectives for one-syllable words?
For one-syllable adjectives, add -er to the end. For example, “tall” becomes “taller.”
3 – Can I use “more” and “-er” together in a comparative adjective?
No, you should not use “more” and “-er” together. For example, it should be “This is faster than that,” not “This is more faster than that.”
4 – What happens to adjectives ending in “-y” when they are made comparative?
When adjectives end in “-y,” change the “-y” to “-i” and add -er. For example, “happy” becomes “happier.”
5 – How do I form superlative adjectives for one-syllable words?
For one-syllable adjectives, add -est to the end. For example, “tall” becomes “tallest.”
6 – Can I use “the most” with one-syllable adjectives in the superlative form?
No, “the most” is used for adjectives with two or more syllables. For one-syllable adjectives, you use -est.
Conclusion:
Comparative and superlative adjectives are essential tools for describing and comparing the world around us. By following the simple rules and practicing with examples, you can use all sorts of adjectives confidently and correctly. Remember, learning English grammar takes time and practice, so don’t be afraid to make mistakes. Keep comparing, keep learning, and soon you’ll be an expert at using these adjectives naturally in your speech and writing!
You May also like