Parts of speech are the categories of words that help us create and understand sentences. They are essential for structuring sentences in a meaningful way. By learning about the different parts of speech, you will improve your ability to speak and write clearly in English. In this article, we will explain each part of speech, its types, and how to use them properly.
Contents
What Are Parts of Speech?
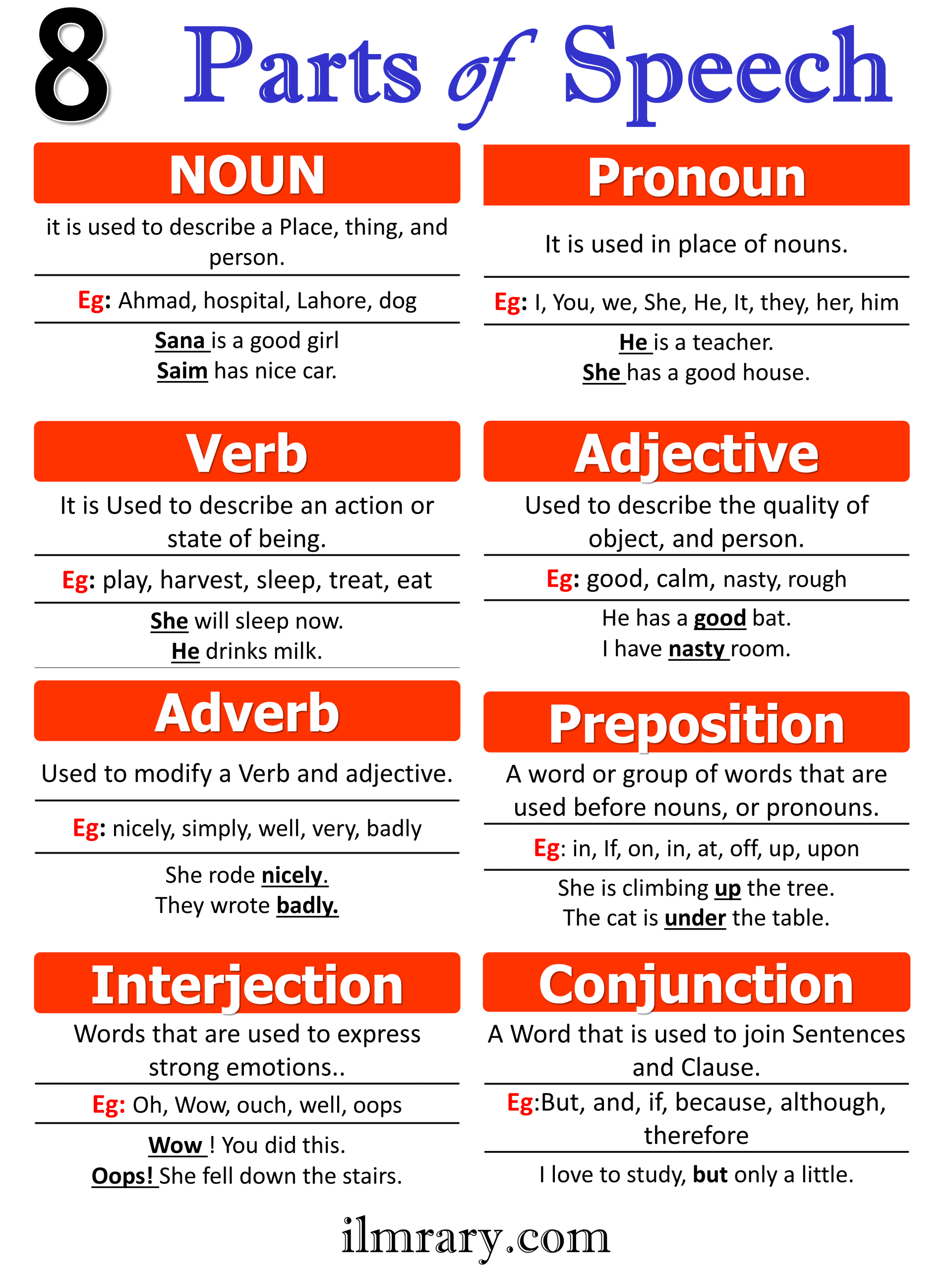
Parts of speech are groups of words that serve different functions in a sentence. Each part of speech has a specific role in the sentence. These roles help to form clear, complete thoughts. The 8 main parts of speech in English are:
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Verb
- Adjective
- Adverb
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
We will now explain each part in detail with examples and types.
1. Noun
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are crucial because they serve as the subject or object in a sentence.
Types of Nouns:
- Common Noun: A general name for a person, place, or thing (e.g., dog, city).
- Proper Noun: A specific name of a person, place, or thing (e.g., Ali, Paris).
- Concrete Noun: Something that can be touched or seen (e.g., apple, chair).
- Abstract Noun: Something that you cannot touch or see (e.g., love, freedom).
- Collective Noun: A word that refers to a group of people or things (e.g., team, family).
Example Sentences:
- Ahmad is a good student.
- She reads a book every day.
- The hospital is near my house.
2. Pronoun
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun. It helps avoid repetition in sentences.
Types of Pronouns:
- Personal Pronouns: Represent specific people or things (e.g., I, you, he, she).
- Possessive Pronouns: Show ownership (e.g., mine, yours, his).
- Reflexive Pronouns: Refer back to the subject (e.g., myself, yourself).
- Relative Pronouns: Connect clauses (e.g., who, which, that).
- Demonstrative Pronouns: Point out specific things (e.g., this, those).
Example Sentences:
- Ali is my friend. He is very kind.
- This is my favorite game.
- They went to the park yesterday.
3. Verb
A verb is a word that shows action or state of being. Verbs are essential for forming sentences because they express what the subject does or experiences.
Types of Verbs:
- Action Verb: Describes a physical or mental action (e.g., run, think).
- Linking Verb: Connects the subject to more information (e.g., am, is, are, was).
- Helping Verb: Supports the main verb (e.g., can, should, will).
Example Sentences:
- Ali is reading a book.
- She can play the piano.
- The dog runs fast in the park.
4. Adjective
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. It gives more detail about a person, place, or thing.
Types of Adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjective: Describes qualities or features (e.g., tall, beautiful).
- Quantitative Adjective: Describes the amount or number (e.g., some, few).
- Demonstrative Adjective: Points to specific things (e.g., this, those).
- Possessive Adjective: Shows ownership (e.g., my, your, his).
- Interrogative Adjective: Used in questions (e.g., which, what).
Example Sentences:
- She has a beautiful dress.
- The big dog barked loudly.
- These apples are fresh.
5. Adverb
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It gives more information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
Types of Adverbs:
- Manner: Describes how an action is done (e.g., quickly, slowly).
- Time: Describes when something happens (e.g., now, later).
- Place: Describes where something happens (e.g., here, there).
- Degree: Describes the intensity of an action (e.g., very, quite).
Example Sentences:
- She speaks very clearly.
- The students worked quickly.
- I will call you tomorrow.
6. Preposition
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence. It helps connect the parts of a sentence.
Types of Prepositions:
- Place: Describes where something is (e.g., on, in, under).
- Time: Describes when something happens (e.g., at, before, after).
- Direction: Describes the direction of action (e.g., to, from, toward).
Example Sentences:
- The cat is under the table.
- We will meet at 5 PM.
- He jumped over the fence.
7. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses. It helps join ideas together in a sentence.
Types of Conjunctions:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: Join two similar elements (e.g., and, but, or).
- Subordinating Conjunctions: Join a dependent clause to an independent clause (e.g., because, although, since).
- Correlative Conjunctions: Used in pairs to connect elements (e.g., either…or, neither…nor).
Example Sentences:
- I like to read and write.
- He didn’t go to the park because it was raining.
- Either you come with me, or you stay at home.
8. Interjection
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong emotion or feeling. It is usually followed by an exclamation mark.
Example Sentences:
- Wow, that was amazing!
- Ouch, that hurts!
- Hey, look at this!
Summary Table of Parts of Speech
| Part of Speech | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Noun | Names a person, place, thing, or idea | Ahmad, hospital, dog, love |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | he, she, they, it |
| Verb | Expresses action or state of being | run, jump, is, are |
| Adjective | Describes or modifies a noun or pronoun | beautiful, tall, happy |
| Adverb | Describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb | quickly, very, softly |
| Preposition | Shows the relationship between a noun and another word | in, on, under, at |
| Conjunction | Connects words, phrases, or clauses | and, but, because, although |
| Interjection | Expresses a strong feeling or emotion | Wow!, Ouch!, Hey! |
Importance of Learning Parts of Speech
Parts of speech are important because they help us organize words into categories like nouns, verbs, adjectives, and more, making it easier to build clear and meaningful sentences. By understanding these roles, we can communicate better, write more effectively, and improve our grammar, ensuring our ideas are expressed correctly and understood by others.
FAQs:
1. What is the role of a noun in a sentence?
A noun acts as the subject or object in a sentence. It names a person, place, thing, or idea. For example, in the sentence “Ali is playing football,” Ali is the noun and the subject of the sentence.
2. How do pronouns make sentences clearer?
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. For example, instead of saying “Ali went to Ali’s house,” you can say “Ali went to his house,” where his is the pronoun replacing Ali’s.
3. Why are verbs important in English?
Verbs describe actions or states of being. Every sentence needs a verb to show what the subject is doing or how the subject is feeling. For example, in “The boy sings,” sings is the verb.
4. Can adjectives and adverbs be used together?
Yes, adjectives describe nouns, and adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. For example, “She is a beautiful dancer” (adjective) and “She dances gracefully” (adverb).
5. What is the difference between a preposition and a conjunction?
A preposition shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and another word in the sentence, like “under” or “before.” A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses, like “and” or “but.”
You May Also Like