Modal verbs in English grammar are key building blocks of English sentences. They help us in explaining different things like a possibility, permission, obligation, and ability, without needing complicated structures. In this article, we will discuss what modal verbs are, look at examples of how they work, and learn how to avoid common mistakes when using them.
Whether you want to improve your existing skills, learning modal verbs will give you more confidence in both spoken and written English. Let’s find out how these special helping verbs can make your communication clearer and more effective!
Contents
What Are Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs are a special type of helping verb used to give extra meaning to the main verb in a sentence. They don’t stand alone but work together with other verbs to show things like possibility, necessity, or ability.
Moreover, they simplify communication by helping speakers express a wide range of ideas without having to use complex sentences. For beginners, understanding these verbs is a critical step toward improving fluency in English.
These verbs are unique because they don’t follow the same rules as regular verbs. For example, they don’t take “-s,” “-ing,” or “-ed” endings, and they are always followed by the base form of another verb.
Here are some common modal verbs:
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Must
- Shall
- Should
- Will
- Would
For Example:
- I can swim. (shows ability)
- You should eat healthy food. (gives advice)
- It might rain tomorrow. (shows possibility)
How to Use Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs are easy to use once you understand the rules. Let’s break them down step by step:
1. No “s” or “ed” Forms
Modal verbs don’t change for different subjects or tenses. For example:
✅ Ali can play football.
❌ Ali cans play football.
In the correct sentence, “can” remains the same regardless of the subject.
2. Always Followed by a Base Verb
Modal verbs are always followed by the base form of the main verb (without “to”).
✅ You must finish your homework.
❌ You must to finish your homework.
3. Negative Form
To make a sentence negative, add not after the modal verb.
✅ I cannot (can’t) go to the party.
✅ You should not (shouldn’t) eat junk food.
4. Question Form
To form a question, place the modal verb at the beginning of the sentence.
✅ Can you help me?
✅ Should I call her?
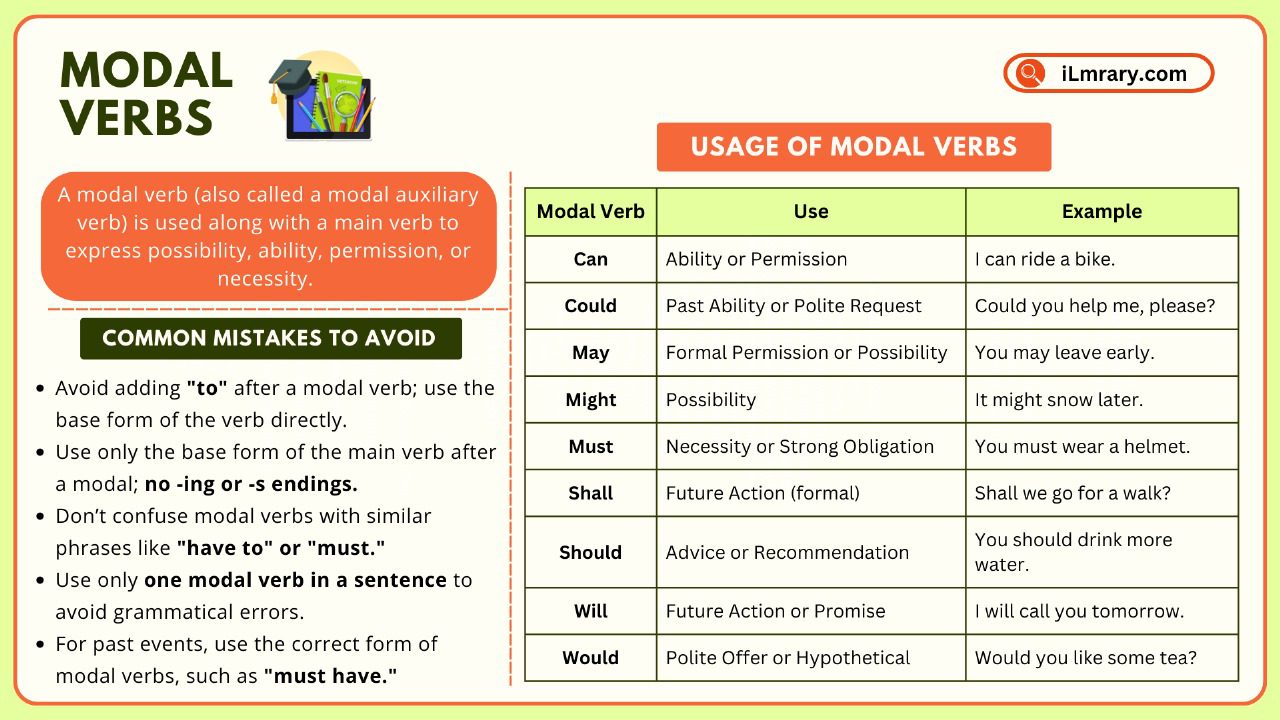
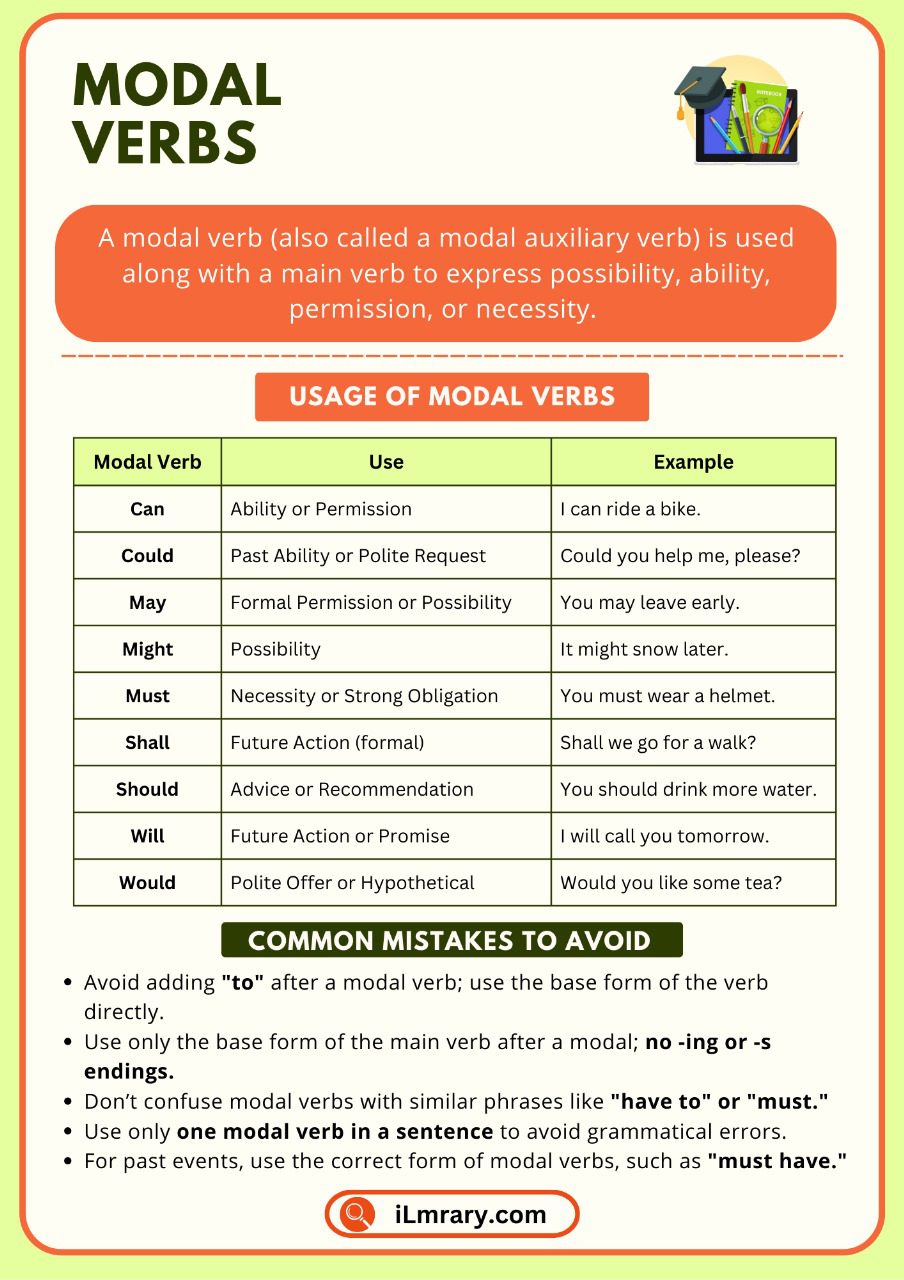
Examples of Modal Verbs with Uses
Here is a table to help you understand different modal verbs and their meanings:
| Modal Verb | Use | Example |
| Can | Ability or Permission | I can ride a bike. |
| Could | Past Ability or Polite Request | Could you help me, please? |
| May | Formal Permission or Possibility | You may leave early. |
| Might | Possibility | It might snow later. |
| Must | Necessity or Strong Obligation | You must wear a helmet. |
| Shall | Future Action (formal) | Shall we go for a walk? |
| Should | Advice or Recommendation | You should drink more water. |
| Will | Future Action or Promise | I will call you tomorrow. |
| Would | Polite Offer or Hypothetical | Would you like some tea? |
Thus, when using these verbs, remember to pay attention to the context. For example, “can” might indicate ability in one sentence (I can swim) but permission in another (Can I go out?).
Modal Verbs in English
Using Modal Verbs in the Past
Modal verbs also allow you to refer to events that have already happened. When combined with have plus the past participle of the main verb, they express certainty, possibility, or regret about situations in hindsight. Below we are going to explain how each form conveys a different degree of meaning.
⇒ Must have
This form shows a strong assumption about a past event.
- Ali must have left early.
- This means there is strong evidence that Ali left before the usual time.
⇒ Should Have
This expresses regret or criticism about a past action.
- I should have checked the weather.
- This means not checking the weather led to a negative outcome.
⇒ Could Have
This indicates a missed opportunity or possibility in the past.
- They could have taken the earlier train.
- This means the option was available, but they didn’t take it.
Common Mistakes with Modal Verbs
Here are some mistakes learners often make and how to avoid them:
1. Adding “to” After a Modal Verb
Modal verbs are always followed by the base form of the verb, not “to.”
❌ You must to finish your homework.
✅ You must finish your homework.
2. Using the Wrong Form of the Main Verb
Modal verbs are followed by the base form of the verb, not -ing or -s endings.
❌ She can sings beautifully.
✅ She can sing beautifully.
3. Confusing Modal Verbs with Similar Words
For example, “have to” and “must” have similar meanings but are used differently.
❌ I have to can go there.
✅ I can go there.
4. Overusing Modals in One Sentence
Only one modal verb should be used in a sentence.
❌ You should must listen to him.
✅ You must listen to him.
5. Using Modal Verbs for Past Events Without the Right Form
When referring to the past, use the correct form.
❌ He must finish the project yesterday.
✅ He must have finished the project yesterday.
Many learners make similar mistakes when using modal verbs. So, let’s discuss them so you don’t make them when you’re using these verbs.
FAQs:
1 – Can I use two modal verbs in one sentence?
No, only one modal verb is used in a sentence. For example, say You should go instead of You should must go.
2 – What’s the difference between “can” and “may”?
Can is for ability, while may is for permission.
- I can swim. (ability)
- You may leave now. (permission)
3 – Are modal verbs used in all tenses?
Most modal verbs don’t change for past or future tenses, but you can use related expressions like had to (past of must).
4 – How can I practice modal verbs daily?
Make sentences about your day, ask questions, and try to observe modals in conversations and media.
5 – Is “ought to” a modal verb?
Yes, it is, but it’s less common than others. It is used for advice, similar to “should.”
Conclusion
To sum up, modal verbs are an essential part of English grammar that helps us express ourselves in different situations. So, by learning their uses, following simple rules, and avoiding common mistakes, you’ll become more confident in your English communication. Practice daily, stay curious, and don’t hesitate to ask questions as you learn. As I have said before, they might seem tricky at first, but with time, you’ll master them!
You May Also Like