Contents
What is an Adverb?
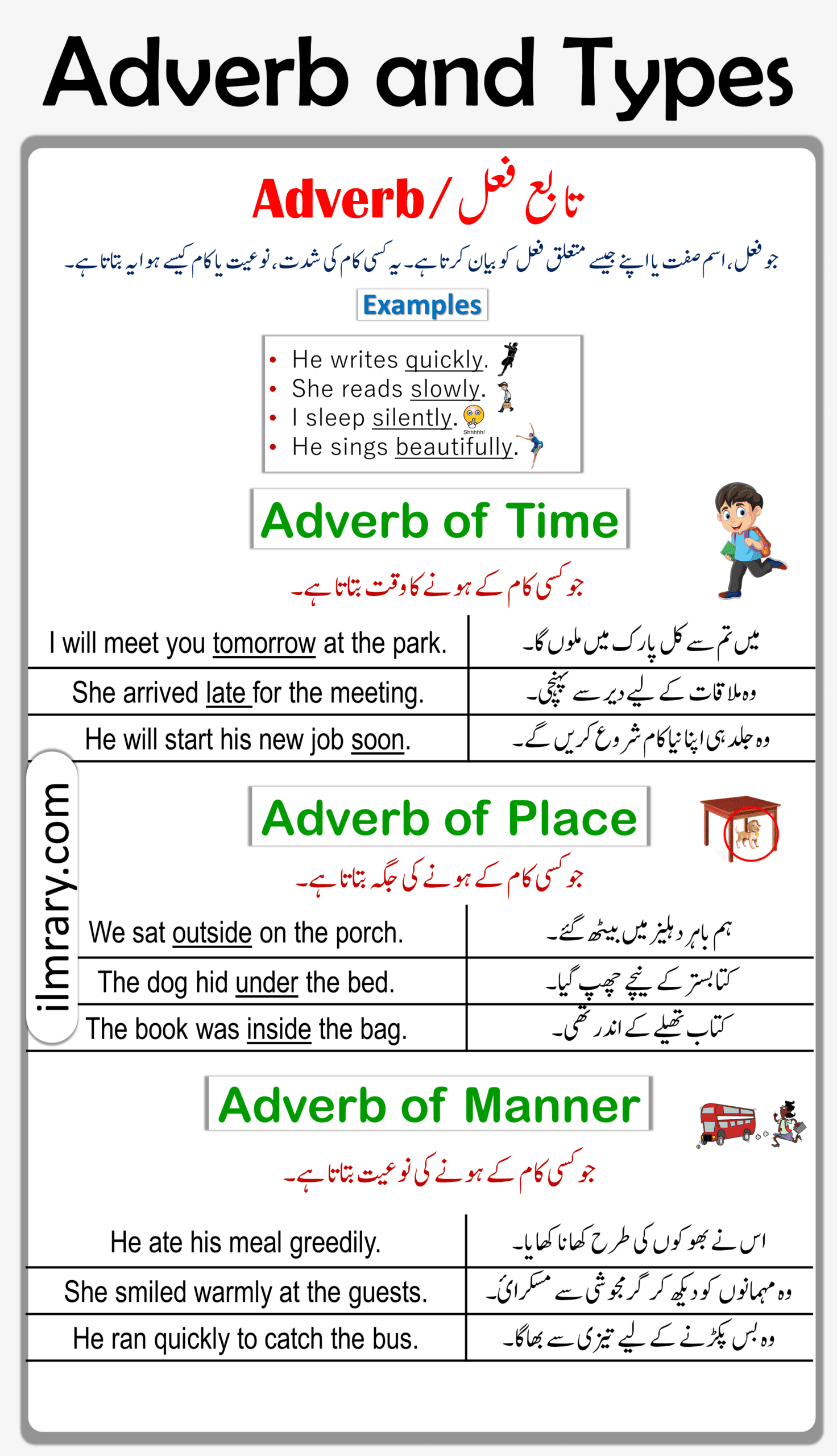
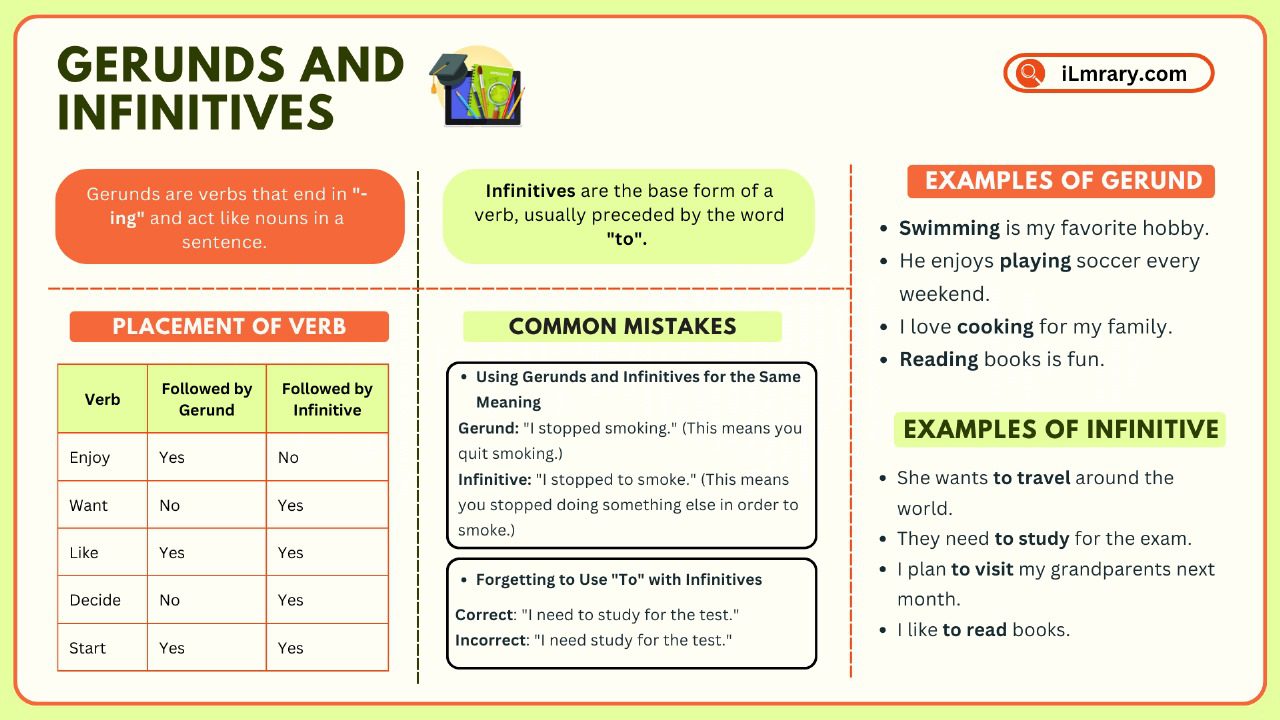
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It provides information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs or an attribute exists. Adverbs often end in “-ly” in English, but there are also adverbs that do not follow this pattern.
وہ لفظ ہے جو فعل، صفت یا دوسری تابع فعل کی ترمیم یا بیان کرتا ہے۔ یہ معلومات فراہم کرتا ہے کہ کس طرح، کب، کہاں یا کتنی حد تک کوئی عمل واقع ہوتا سے ختم ہوتے ہیں، لیکن ایسی بھی تابع فعل جو اس پیٹرن کی پیروی نہیں کرتے۔
Examples of Adverbs (تابع فعل کی مثالیں)
- He sings beautifully. (وہ خوبصورتی سے گاتا ہے۔)
- She spoke softly. (وہ نرمی سے بولی۔)
- They arrived late. (وہ دیر سے پہنچے۔)
- The cat jumped high. (بلی بلندی سے کودی۔)
- He runs fast. (وہ تیزی سے دوڑتا ہے۔)
- She dances gracefully. (وہ خوش اندامی سے ناچتی ہے۔)
- They played outside. (وہ باہر کھیلے۔)
- The car stopped suddenly. (گاڑی اچانک رک گئی۔)
- He speaks English fluently. (وہ انگریزی فصیحے سے بولتا ہے۔)
- She laughed loudly. (وہ بلند آواز میں ہنستی ہے۔)
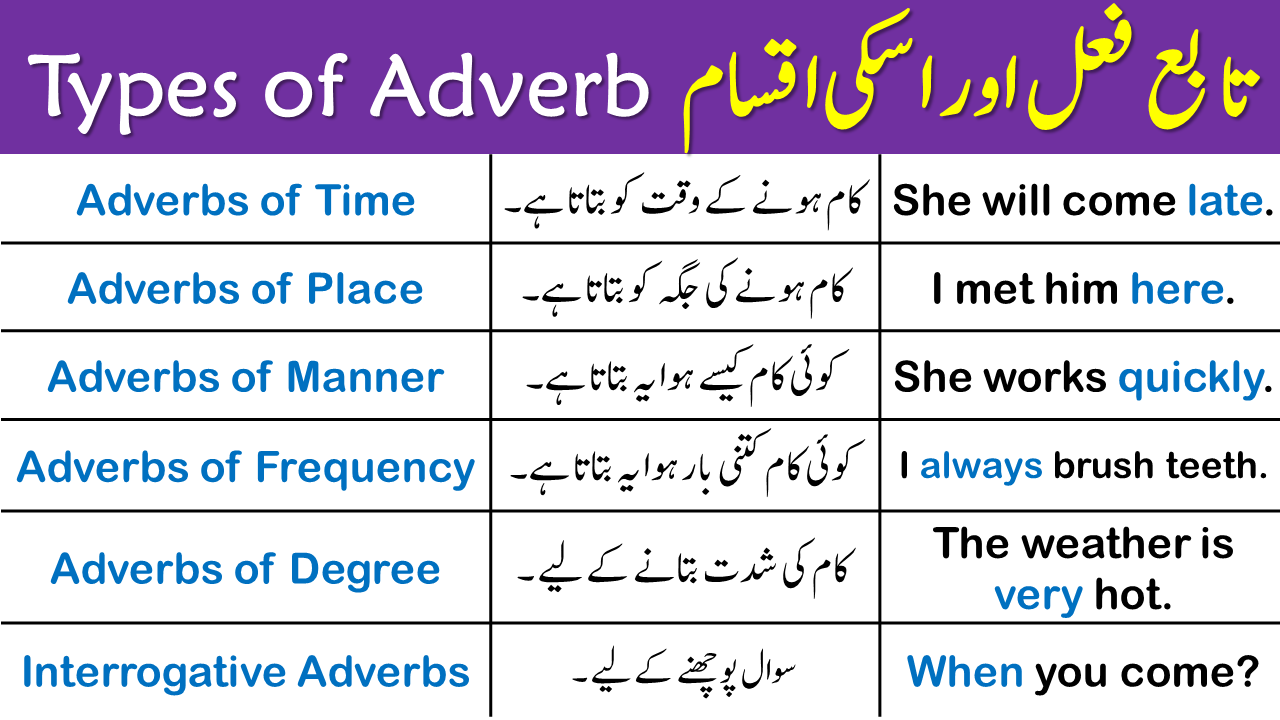
Types of Adverb:
- Adverbs of Time
- Adverbs of place
- Adverbs of manner
- Adverbs of frequency
- Adverbs of degree
- interrogative adverbs
- Relative adverbs
1. Adverbs of Time (وقت کے قواعد)
Adverbs of time indicate when an action occurs.
Examples words: “now” (ابھی), “later” (بعد میں), and “always” (ہمیشہ). Adverbs of time help us establish the temporal context of an event.
Example Sentences:
- I will meet you tomorrow at the park.
- She arrived late for the meeting.
- They go to the gym every day to exercise.
- We had dinner last night at a fancy restaurant.
- He will start his new job soon.
2. Adverbs of Place (جگہ کے قواعد)
Adverbs of place describe where an action takes place. They provide information about the location or position of an event.
Example words: “here” (یہاں), “there” (وہاں), and “everywhere” (ہر جگہ).
Example Sentences:
- She placed the book here on the table.
- The birds flew there to build their nests.
- The children searched everywhere for their lost toy.
- The museum exhibits showcased art from around the world.
- We walked outside in the park, enjoying the fresh air.
3. Adverbs of Manner (طریقہ کے قواعد)
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed or the way something happens. They often end in “-ly” in English.
For instance, “quickly” (تیزی سے), “carefully” (محتاطی سے), and “happily” (خوشی سے) are adverbs of manner.
Example Sentences:
- She danced gracefully across the stage.
- He spoke loudly to ensure everyone could hear him.
- The dog wagged its tail happily upon seeing its owner.
- The children ran playfully in the park, laughing and chasing each other.
- The chef carefully sliced the vegetables precisely to create a beautifully presented dish.
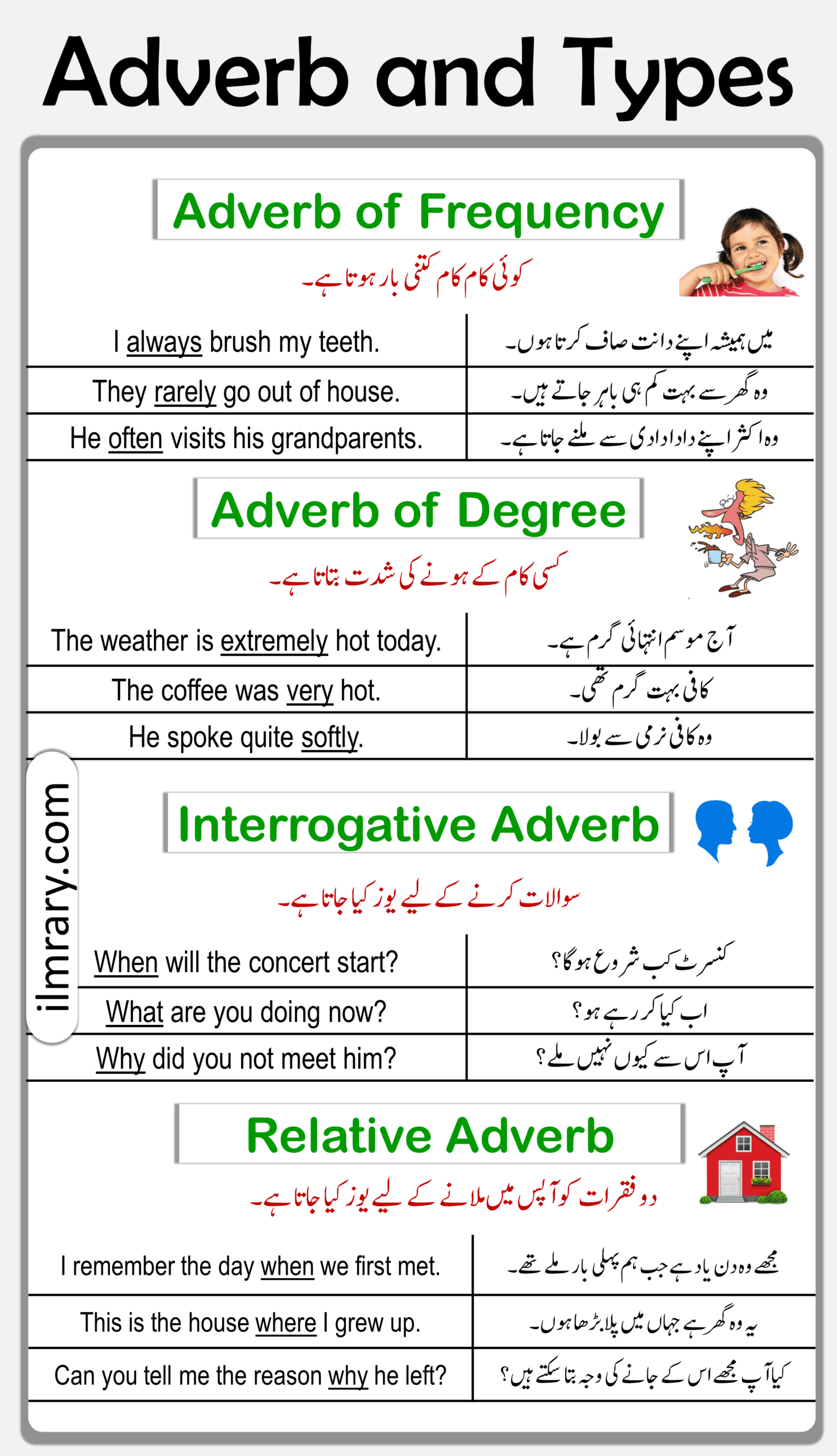
4. Adverbs of Frequency (تعداد کے قواعد)
Adverbs of frequency indicate how often an action occurs. They express the frequency of an event,
such as “always” (ہمیشہ), “often” (اکثر), and “rarely” (کمی).
Example Sentences:
- I always brush my teeth before going to bed.
- She often visits her grandparents on the weekends.
- They rarely eat fast food because they prefer homemade meals.
- He sometimes takes the bus to work instead of driving.
- We never miss our favorite TV show on Thursday nights.
5. Adverbs of Degree (درجہ کے قواعد)
Adverbs of degree modify adjectives or adverbs, indicating the intensity or extent of an action or quality.
Example words: “very” (بہت), “extremely” (بہت زیادہ), and “quite” (کافی).
Example Sentences:
- She is very tall compared to her classmates.
- The weather is extremely hot today.
- He was quite tired after running the marathon.
- The movie was incredibly exciting and kept me on the edge of my seat.
- They were absolutely delighted with the surprise party.
6. Interrogative Adverbs (سوالیہ قواعد)
Interrogative adverbs are used to ask questions.
Example words: “why” (کیوں), “where” (کہاں), and “how” (کیسے). These adverbs help in seeking information.
Example Sentences:
- Why did you miss the meeting yesterday?
- Where is the nearest grocery store?
- When will the concert start?
- How did you solve that difficult math problem?
- What are you doing this weekend?
7. Relative Adverbs (نسبی قواعد)
Relative adverbs introduce relative clauses and relate to a noun or pronoun in the main clause.
Example words: “when” (جب), “where” (جہاں), and “why” (کیوں).
Example Sentences:
- I remember the day when we first met.
- This is the house where I grew up.
- Can you tell me the reason why he left?
- That’s the restaurant where we had our first date.
- I will never forget the moment when I won the championship.
You May Also Like